Cursive writing, often regarded as a beautiful and fluid style of handwriting, has been a traditional method of writing for centuries. Characterised by its connected letters and elegant loops, cursive writing is not just a form of calligraphy but a practical skill with numerous benefits. In this blog post, we will explore what cursive writing is, how to write in cursive, its benefits, and provide examples to help you master this artful style.
What is Cursive Writing?
Cursive writing is a style of penmanship where letters are connected in a flowing manner. Unlike print writing, where each letter is distinct and separate, cursive writing emphasises continuous strokes, resulting in a more fluid and cohesive appearance. The primary goal of cursive writing is to increase writing speed and legibility while maintaining a graceful and connected form.
How to Write in Cursive
Learning how to write in cursive involves mastering a few fundamental techniques. Here’s a step-by-step guide to get you started:
Familiarise Yourself with Cursive Letters
Begin by studying the cursive alphabet. Each letter has a unique form, and many letters are connected in a distinctive way. Practice writing each letter individually before combining them.
Practice Letter Connections
In cursive writing, letters are often connected. Focus on how different letters join together. For instance, the end of one letter might smoothly transition into the beginning of the next. Practice writing common letter combinations and words to get accustomed to the flow.
Use Proper Hand Positioning
Hold your pen comfortably and ensure your hand is positioned in a way that allows smooth movement across the paper. A relaxed grip can help improve the fluidity of your cursive writing.
Start with Simple Words
Once you’re comfortable with individual letters, start practising simple words. Write slowly and deliberately to maintain the connection between letters. Gradually increase your writing speed as you gain confidence.
Consistent Practice
Like any skill, cursive writing improves with regular practice. Set aside time each day to practice writing in cursive, and use lined paper to keep your letters consistent and properly aligned.
Benefits of Cursive Writing
Cursive writing offers several benefits that extend beyond aesthetics. Here are some key advantages:
Improved Fine Motor Skills
Writing in cursive requires precise hand movements and coordination. Practising cursive can enhance fine motor skills, which are crucial for tasks that involve hand-eye coordination.
Enhanced Writing Speed
Cursive writing allows for a more fluid and continuous flow of words, which can increase writing speed compared to print writing. This can be particularly useful in settings where speed is essential, such as note-taking during lectures.
Better Retention and Cognitive Benefits
Research suggests that cursive writing may improve memory retention and cognitive processing. The act of writing in cursive engages different parts of the brain, which can aid in information retention and comprehension.
Personal Expression and Aesthetics
Cursive writing has a unique aesthetic appeal. The flowing and connected nature of cursive can add a personal touch to handwritten notes, invitations, and other documents.
Legibility in Certain Contexts
In some cases, cursive writing can be more legible than print, especially when it comes to connecting letters and maintaining consistent letter height and spacing.
Why Cursive Writing is Important
Despite the rise of digital communication, cursive writing remains important for several reasons:
- Historical and Cultural Significance: Cursive writing has a rich historical and cultural significance. Many historical documents, letters, and manuscripts were written in cursive, and understanding this style of writing connects us to the past.
- Educational Development: Learning cursive writing can be a valuable part of education. It helps students develop fine motor skills, hand-eye coordination, and a sense of discipline and patience.
- Personal and Professional Use: Cursive writing can be used in personal and professional contexts, such as signing documents, writing personal letters, and creating decorative invitations. It adds a personal and formal touch that digital text cannot replicate.
- Cognitive Development: The process of learning cursive writing involves complex cognitive processes, including spatial awareness and memory. This can contribute to overall cognitive development and problem-solving skills.
Examples of Cursive Writing
To help you visualise cursive writing, here are a few examples of how different letters and words look in cursive:
Individual Letters: Each letter in cursive has a unique shape and flow. For example, the letter “a” might start with a loop and connect smoothly to the following letter, while “b” features a vertical stroke with a rounded loop.

Common Words: Practice writing common words in cursive to see how letters connect. For instance, “hello” in cursive might look like this: h-e-l-l-o, with each letter flowing into the next.
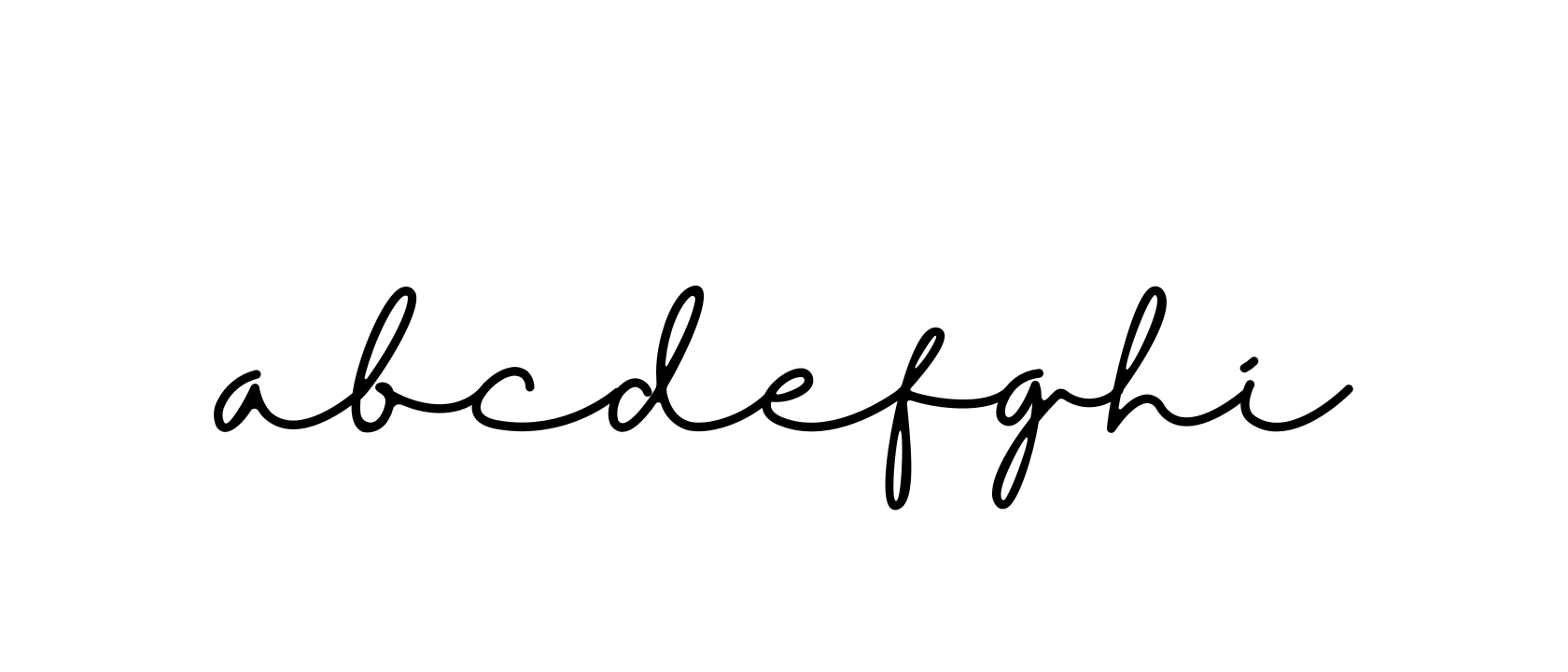
Signature Examples: Cursive writing is often used in signatures. Practice writing your name in cursive to develop a personal and elegant signature style.

Also read: Tips for Writing a Good University Essay
Conclusion
Cursive writing is a timeless skill that combines elegance with practicality. Whether you’re learning cursive for personal enjoyment, educational purposes, or professional use, mastering this artful form of writing can offer numerous benefits. From enhancing fine motor skills to improving writing speed and cognitive development, cursive writing remains a valuable and meaningful skill.
If you’re embarking on an academic journey and need support, we can assist you with everything from tutoring sessions to coursework writing services for assignments. Contact us to ensure your academic work is polished and professionally presented.




